Explore the workings of voltage multipliers, their types, and diverse applications in electronics and power transmission.
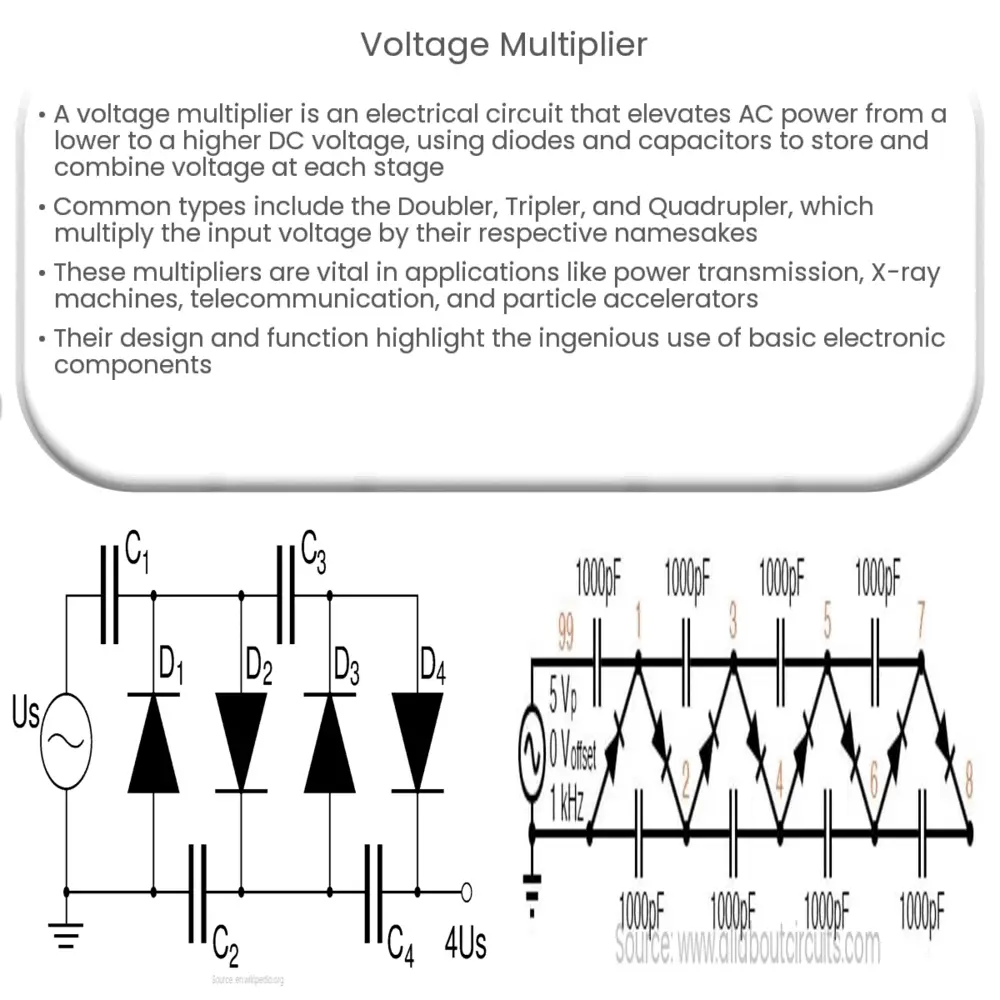
Voltage Multiplier: An Overview
A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage level to a higher DC voltage level. It’s a specialized form of rectifier circuit that delivers an output voltage that is a multiple of the peak input voltage.
Principle of Operation
Voltage multipliers primarily operate on a straightforward principle. They use diodes and capacitors to generate a higher output voltage by storing and adding together the voltage in each stage, hence the name “multiplier”.
- Diodes: These are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction only. In a voltage multiplier, diodes are used to direct the flow of charge and prevent its return, ensuring that the charge accumulates over the stages.
- Capacitors: These are electrical components that store electrical energy in an electric field. In a voltage multiplier, capacitors are used to store and release energy at specific times to add to the overall voltage.
Types of Voltage Multipliers
There are several types of voltage multipliers, depending on the specific application or requirements. The most common types are the Doubler, Tripler, and Quadrupler. Each one multiplies the input voltage by a factor corresponding to its name.
- Doubler: A voltage doubler receives an input voltage and outputs a voltage that is approximately twice the peak input voltage. The simplest form of a voltage doubler is the half-wave voltage doubler, which uses two diodes and two capacitors.
- Tripler: A voltage tripler, as the name implies, triples the input voltage. It is essentially composed of a doubler and an additional stage that adds to the voltage.
- Quadrupler: This type multiplies the input voltage by four. It essentially combines two doubler stages.
In each of these types, the circuit arrangement and the number of diodes and capacitors vary. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the working and applications of these multipliers.
Working of Voltage Multipliers
The working of a voltage multiplier is sequential and depends on the AC cycle. For instance, in a half-wave doubler, during the positive half cycle, the first diode conducts, charging the first capacitor to the peak voltage. In the negative half cycle, the second diode conducts, charging the second capacitor. The total voltage, therefore, is twice the peak input voltage.
Similarly, in a tripler or quadrupler, the sequence of charging and discharging of capacitors during different cycles results in the multiplication of voltage. The multiplication factor depends on the number of stages in the multiplier.
Applications of Voltage Multipliers
Voltage multipliers have a wide range of applications, particularly where high voltages are required. Some key applications include:
- Power Transmission: They are used to step up voltages for long-distance power transmission to reduce power loss.
- X-ray Machines: High voltages are required for generating X-rays. Voltage multipliers play a crucial role in these medical devices.
- Telecommunication: They are used in telecommunication devices to amplify signals for better reception and transmission.
- Particle Accelerators: In scientific research, voltage multipliers are used in particle accelerators to achieve the high voltages required to accelerate particles to near-light speeds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, voltage multipliers serve as an indispensable tool in the field of electronics, playing a significant role in various applications ranging from power transmission to scientific research. By understanding the working of voltage multipliers, we can appreciate the simple yet ingenious application of diodes and capacitors to multiply voltages. As advancements in technology continue, the potential uses and improvements of voltage multipliers are limitless, promising exciting developments in the future.